With the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) MySQL Database Services, in order to connect you have to access MySQL through a compute node. This means you will have to create a compute node within OCI. You can do this quickly with Terraform (here).
Once you have an OCI compute node built, you will need to install MySQL Shell. MySQL Shell is the advanced MySQL Client for Developers and DBAs. Making interaction with MySQL easier from the command line.
Installing MySQL Shell
Access the OCI compute node (needs public IP address of compute node)
> ssh -I .ssh/mysql_private_key.pem opc@<public IP address>
Install MySQL Shell via command line
> sudo yum install -y mysql-shell
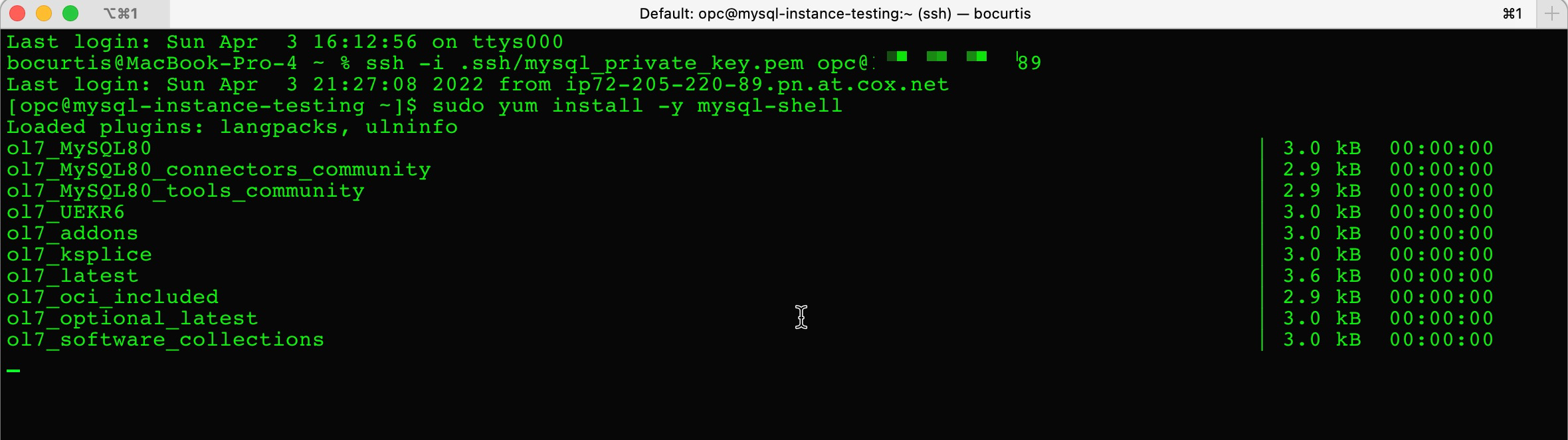
After MySQL Shell is installed, you can access your MySQL Database Service (database) via the command line.
Connecting to MySQL
To start MySQL Shell and connect to the DB System endpoint, the following command is used. Keep in mind, you are SSHed into the compute node, from the compute node you’ll use the DB System private IP address to connect.
> mysqlsh [email protected]
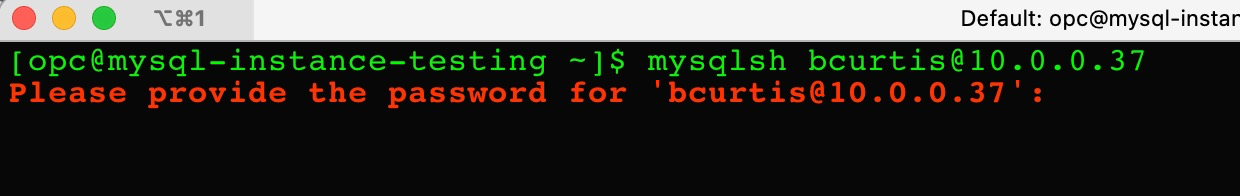
Provide the password for the user that was established when creating the MySQL Database Service.
After providing the password, you will be connected to the MySQL Database Service. By default the MySQL Shell will connect you to the JavaScript command line option. I’ve switched to the SQL command line option by using “\sql”.
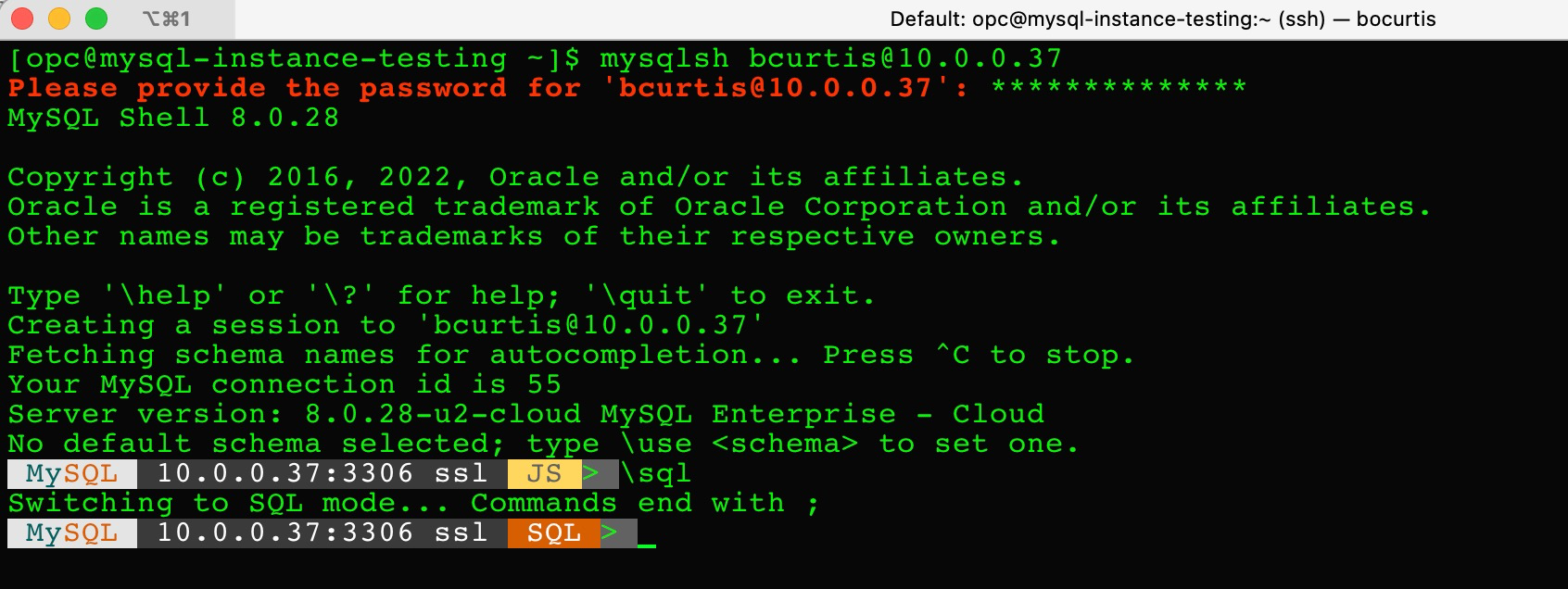
At this point, you can now interact with your MySQL database on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Bobby Curtis

I’m Bobby Curtis and I’m just your normal average guy who has been working in the technology field for awhile (started when I was 18 with the US Army). The goal of this blog has changed a bit over the years. Initially, it was a general blog where I wrote thoughts down. Then it changed to focus on the Oracle Database, Oracle Enterprise Manager, and eventually Oracle GoldenGate.
If you want to follow me on a more timely manner, I can be followed on twitter at @dbasolved or on LinkedIn under “Bobby Curtis MBA”.
